Flume基础学习
Flume基础学习(一)
Flume日志采集工具,可以配合第三方的前端埋点SDK去实现行为日志采集,到目前为止在工作中也没有使用到和涉及到。当时在使用这个工具时,学习的内容的深度相对来说也比较浅薄。后续会根据学习内容和规划做相应的调整,完善相关的学习笔记。本文主要介绍了Flume工具的基本配置使用、各个组件在其中发挥的作用、内部架构等。
一、Flume概述:
1、定义:
Flume是Cloudera提供的一个高可用的,高可靠的,分布式的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统。Flume基于流式架构,灵活简单。
2、Flume架构

agent:
- Agent是一个JVM进程,它以事件的形式将数据从源头送至目的。
- Agent主要有3个部分组成,Source、Channel、Sink。
source
Source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件。Source组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、 taildir 、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。
sink
- Sink不断地轮询Channel中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个Flume Agent。
- Sink组件目的地包括hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、HBase、solr、自定义。
channel
- Channel是位于Source和Sink之间的缓冲区。因此,Channel允许Source和Sink运作在不同的速率上。Channel是线程安全的,可以同时处理几个Source的写入操作和几个Sink的读取操作。
- Flume自带两种Channel:Memory Channel和File Channel。
- Memory Channel是内存中的队列。Memory Channel在不需要关心数据丢失的情景下适用。如果需要关心数据丢失,那么Memory Channel就不应该使用,因为程序死亡、机器宕机或者重启都会导致数据丢失。
- File Channel将所有事件写到磁盘。因此在程序关闭或机器宕机的情况下不会丢失数据。
event
传输单元,Flume数据传输的基本单元,以Event的形式将数据从源头送至目的地。Event由Header和Body两部分组成,Header用来存放该event的一些属性,为K-V结构,Body用来存放该条数据,形式为字节数组。
header(k,v) body(byte array)
二、Flume入门
1、安装Flume地址
2、安装部署
hadoop版本3.x要删除lib文件夹下的guava-11.0.2.jar包以兼容Hadoop 3.x
3、官方入门案例
需求:使用Flume监听一个端口,收集该端口数据,并打印到控制台。
安装netcat工具
1
sudo yun install -y nc
创建Flume Agent配置文件flume-netcat-logger.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22添加内容如下:
# Name the components on this agent #a1表示agent的名字
a1.sources = r1 ##r1表示a1 agent一个source的名字
a1.sinks = k1 ##k1表示a1 agent一个sink的名字
a1.channels = c1 ##c1表示a1 agent一个channel的名字
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat ##表示r1 source的类型也就是输入源的类型
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost ##要监听的主机的IP
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 ###要监听的端口号是多少
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger ##a1的数据输出的目的地是控制台
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory ##表示a1 channel的类型是memory内存型
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 ##表示a1 channel的事件容量是1000条
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 ##表示a1的channel收集到100条event后再去提交事务
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 ##表示吧r1和c1连接起来
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 ##表示把k1和c1连接起来启动flume
1
bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/flume-netcat-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
1
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf/ -n a1 -f job/flume-netcat-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
参数说明:
–conf/-c:表示配置文件存储在conf/目录
–name/-n:表示给agent起名为a1
–conf-file/-f:flume本次启动读取的配置文件是在job文件夹下的flume-telnet.conf文件。
-Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console :-D表示flume运行时动态修改flume.root.logger参数属性值,并将控制台日志打印级别设置为INFO级别。日志级别包括:log、info、warn、error。
#实时监控单个追加文件案例。
需求说明:实时监控Hive日志,并上传到HDFS中
配置文件编写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95##自己编写的配置
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks=k1
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.positionFile =/home/hdfs/flume/taildir_position.json
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /home/hdfs/flume/data/.*\.txt
a1.sinks.k1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://master:8020/flume/events/%Y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events-
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
#####################################################################################################
#####################################################################################################
#案例
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r2
a2.sinks = k2
a2.channels = c2
# Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r2.type = exec
a2.sources.r2.command = tail -F /opt/module/hive/logs/hive.log
# Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k2.type = hdfs
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://master:8020/flume/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = logs-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 60
#设置每个文件的滚动大小
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a2.channels.c2.type = memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r2.channels = c2
a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2
##########################################################################################################################################################################################################
#案例:
2. 入门案例 2.1 实时监控单个追加文件,将内容打印到控制台
配置文件名字: exec-flume-logger.conf
##name
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
##source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /home/hdfs/test/data.txt
##channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
###sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
##bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
#实时监控目录下多个新文件
案例需求:使用Flume监听整个目录的文件,并上传至HDFS
配置文件编写
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25###我配置写的Spooling Directory Source
spooling-flume-hdfs.conf 配置文件如下
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#sources
a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir
a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /home/hdfs/test/spoolDir
a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true
#sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://master:8020/flume/events/%Y-%m-%d
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = logs-
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = second
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
##channels
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
##bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
474. 入门案例 3 实时监控目录下的新文件,将内容上传到HDFS中
配置文件名字: spooling-flume-hdfs.conf
#Named
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
#Source
a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir
a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /opt/module/flume-1.9.0/jobs/spooling
a1.sources.r1.fileSuffix = .COMPLETED
a1.sources.r1.ignorePattern = .*\.tmp
#Channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
#Sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop102:8020/flume/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = logs-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60
#设置每个文件的滚动大小
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#Bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
#实时监控多个目录下的多个追加文件
Exec source适用于监控一个实时追加的文件,不能实现断点续传;Spooldir Source适合用于同步新文件,但不适合对实时追加日志的文件进行监听并同步;而Taildir Source适合用于监听多个实时追加的文件,并且能够实现断点续传。
案例需求:使用Flume监听整个目录的实时追加文件,并上传至HDFS
配置文件编写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#sources
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /home/hdfs/flume/taildir_position.json
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1 f2
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /home/hdfs/test/data/.*\.txt
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f2 = /home/hdfs/test/data/.*\.log
#sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://master:8020/flume/tail/%Y-%m-%d
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = tail-
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = second
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
##channels
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
#bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
三、Flume进阶
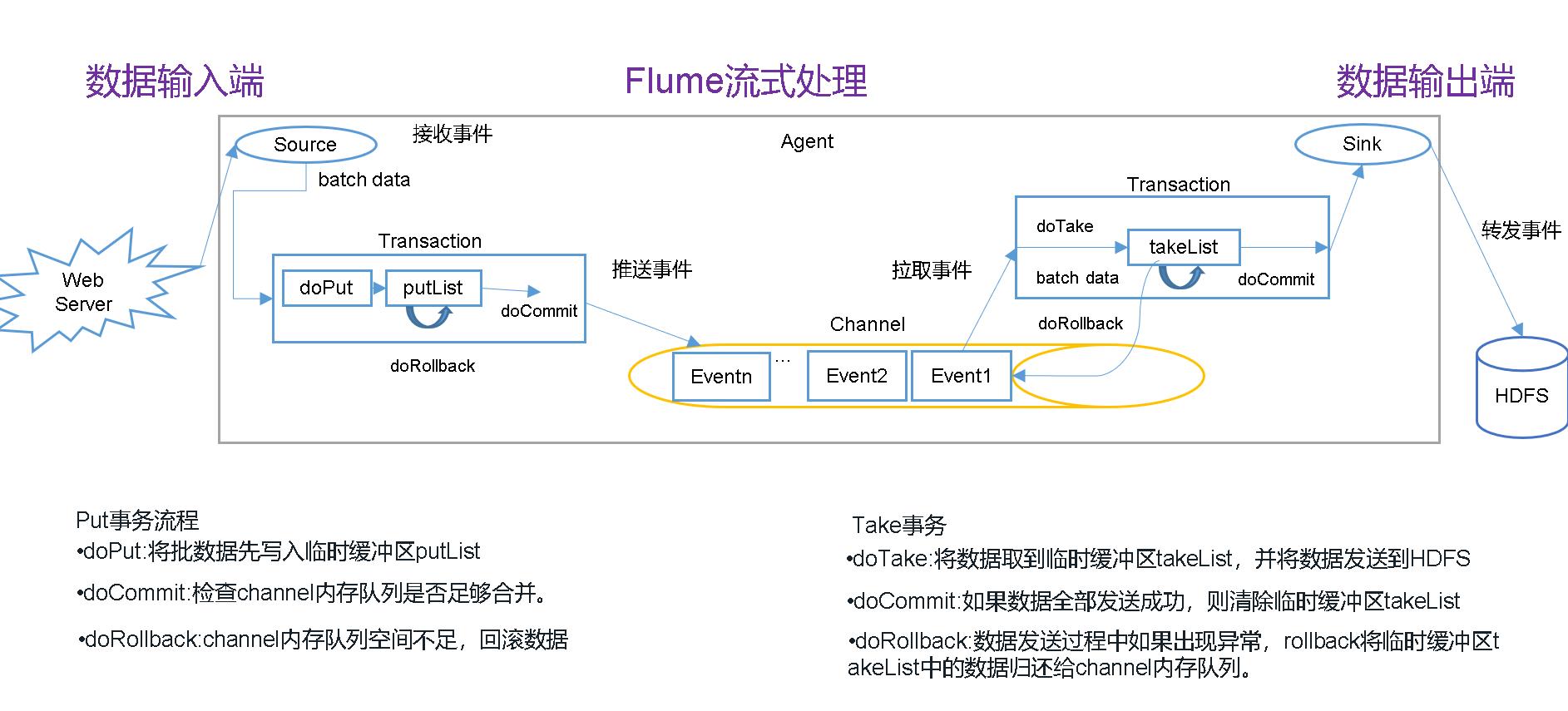
1、Flume事务
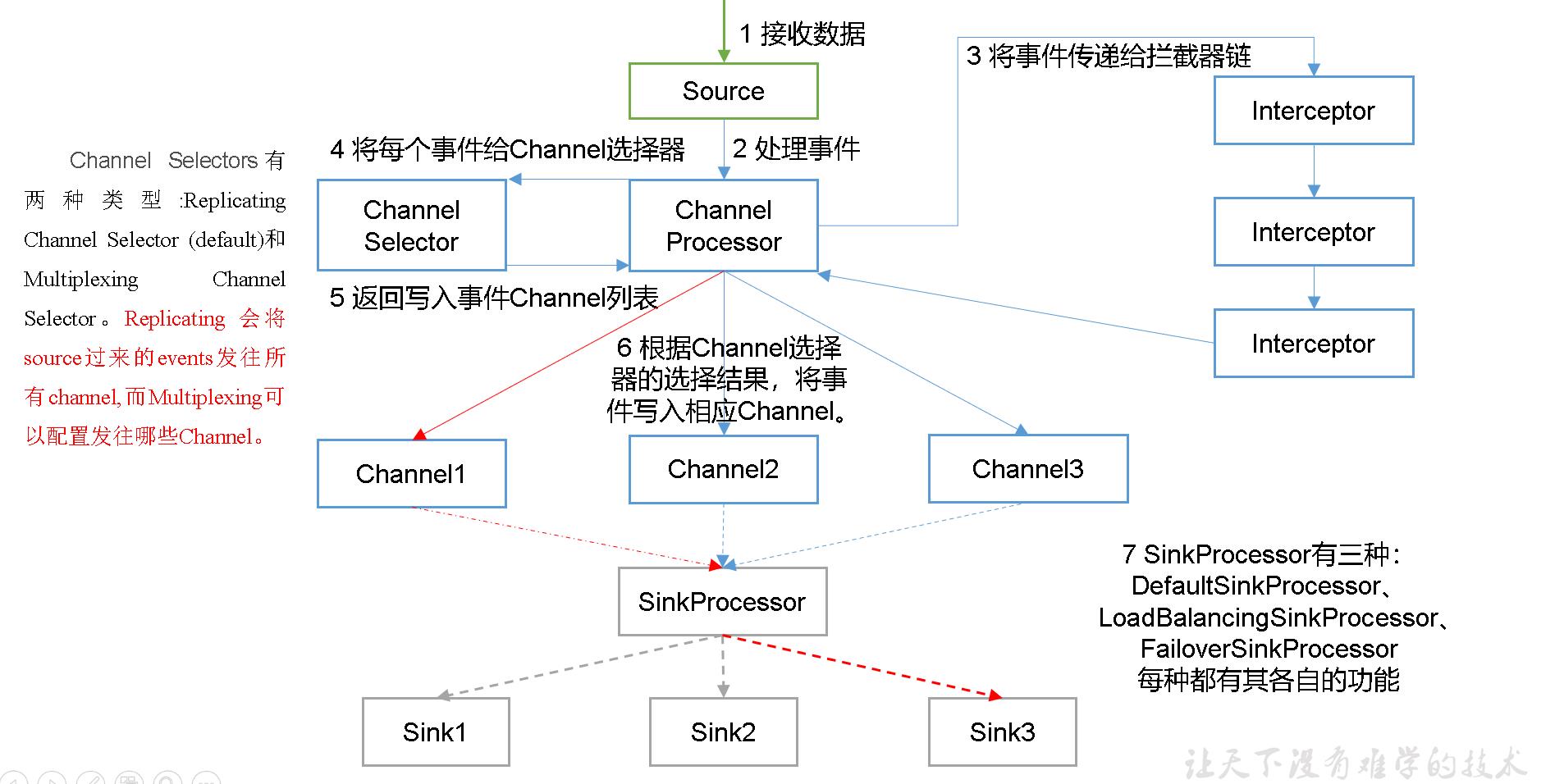
2、Agent内部原理
- source采集到日志服务器或者是端口等的数据时,报数据包装成event
- 在批量的放入临时缓存putlist,并通过channel processor处理事件
- channel processor将事件传递给拦截器链,对事件进行过滤
- 再把事件还回channel processor并将每个事件给channel selector
- 返回写入事件的channel 列表
- 根据channel选择器的结果,将事件写入对应得channel中
- doTake将事件批量的取到sink processor中再通过事务写入到相应的目标中
ChannelSelector
ChannelSelector的作用就是选出Event将要被发往哪个Channel。其共有两种类型,分别是Replicating(复制)和Multiplexing(多路复用)。
ReplicatingSelector会将同一个Event发往所有的Channel,Multiplexing会根据相应的原则,将不同的Event发往不同的Channel。
SinkProcessor
SinkProcessor共有三种类型,分别是DefaultSinkProcessor、LoadBalancingSinkProcessor和FailoverSinkProcessor
DefaultSinkProcessor对应的是单个的Sink,LoadBalancingSinkProcessor和FailoverSinkProcessor对应的是Sink Group,LoadBalancingSinkProcessor可以实现负载均衡的功能,FailoverSinkProcessor可以错误恢复的功能。
3、Flume的拓扑结构
简单串联:这种模式是将多个flume顺序连接起来了,从最初的source开始到最终sink传送的目的存储系统。此模式不建议桥接过多的flume数量, flume数量过多不仅会影响传输速率,而且一旦传输过程中某个节点flume宕机,会影响整个传输系统。
即,一个agent的sink连接另个agent的source
复制和多虑复用:Flume支持将事件流向一个或者多个目的地。这种模式可以将相同数据复制到多个channel中,或者将不同数据分发到不同的channel中,sink可以选择传送到不同的目的地。
负载均衡和故障转移:Flume支持使用将多个sink逻辑上分到一个sink组,sink组配合不同的SinkProcessor可以实现负载均衡和错误恢复的功能。
聚合:
这种模式是我们最常见的,也非常实用,日常web应用通常分布在上百个服务器,大者甚至上千个、上万个服务器。产生的日志,处理起来也非常麻烦。用flume的这种组合方式能很好的解决这一问题,每台服务器部署一个flume采集日志,传送到一个集中收集日志的flume,再由此flume上传到hdfs、hive、hbase等,进行日志分析。
4、Flume开发案例
案例需求:使用Flume-1监控文件变动,Flume-1将变动内容传递给Flume-2,Flume-2负责存储到HDFS。同时Flume-1将变动内容传递给Flume-3,Flume-3负责输出到Local FileSystem。
配置文件编写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97Flume-1
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
#sources
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /home/hdfs/flume/taildir_position.json
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /home/hdfs/test/data/log.log
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
##sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 192.168.157.10
a1.sinks.k1.port = 6666
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = 192.168.157.10
a1.sinks.k2.port = 7777
##channels
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
##bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.r1.channels = c2
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
flume-ng agent -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -n a1 -f ~/confs/flume-01.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
#############################################################################################
Flume-2
#name
a2.sources = r2
a2.sinks = k2
a2.channels = c2
#sources
a2.sources.r2.type = avro
a2.sources.r2.bind = localhost
a2.sources.r2.port = 6666
##sinks
a2.sinks.k2.type = hdfs
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://master:8020/flume/threeflume/%Y-%m-%d
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = log-
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = second
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
##channels
a2.channels.c2.type = memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity = 10000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
##bind
a2.sources.r2.channels = c2
a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2
flume-ng agent -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -n a2 -f ~/confs/flume-02.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
################################################################################################
Flume-3
#name
a3.sources = r3
a3.sinks = k3
a3.channels = c3
#sources
a3.sources.r3.type = avro
a3.sources.r3.bind = localhost
a3.sources.r3.port = 7777
##sinks
a3.sinks.k3.type = file_roll ##采集到的数据放到本地Stores events on the local filesystem.
a3.sinks.k3.sink.directory = /opt/module/flume-1.9.0/jobs/fileroll
##channels
a3.channels.c3.type = memory
a3.channels.c3.capacity = 10000
a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity = 100
##bind
a3.sources.r3.channels = c3
a3.sinks.k3.channel = c3
flume-ng agent -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -n a3 -f ~/confs/flume-03.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console输出的本地目录必须是已经存在的目录,如果该目录不存在,并不会创建新的目录。
#负载均衡和故障转移
使用Flume1监控一个端口,其sink组中的sink分别对接Flume2和Flume3,采用FailoverSinkProcessor,实现故障转移的功能。
使用jps -ml查看Flume进程。
1 | flume01-failover.conf |
- 负载均衡
1 | flume01-balance.conf |
- 聚合
案例需求:hadoop102上的Flume-1监控文件/opt/module/group.log,hadoop103上的Flume-2监控某一个端口的数据流,Flume-1与Flume-2将数据发送给hadoop104上的Flume-3,Flume-3将最终数据打印到控制台。
1 | flume01-aggre.conf |
- 自定义interceptor
需求:使用Flume采集服务器本地日志,需要按照日志类型的不同,将不同种类的日志发往不同的分析系统。
添加maven依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId>
<artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId>
<version>1.9.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>编写interceptor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
public void initialize() { }
public Event intercept(Event event) {
byte[] body = event.getBody();
String s = new String(body, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
if (s.contains("#") || s.contains("*")) {
event.getHeaders().put("type","char");
}else if (s.contains("1")){
event.getHeaders().put("type","num");
}else {
event.getHeaders().put("type","word");
}
return event;
}
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> list) {
for (Event event : list) {
intercept(event);
}
return list;
}
public void close() { }
public static class build implements Interceptor.Builder{
public Interceptor build() {
return new MyInterceptor();
}
public void configure(Context context) { }
}
}编写flume配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139flume01-interceptor.conf
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2 k3
a1.channels = c1 c2 c3
#sources
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = com.suhe.interceptor.MyInterceptor$Builder
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = type
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.char = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.num = c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.word = c3
##sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = localhost
a1.sinks.k1.port = 6666
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = localhost
a1.sinks.k2.port = 7777
a1.sinks.k3.type = avro
a1.sinks.k3.hostname = localhost
a1.sinks.k3.port = 8888
##channels
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c3.type = memory
a1.channels.c3.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c3.transactionCapacity = 100
##bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 c3
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
a1.sinks.k3.channel = c3
flume-ng agent -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -n a1 -f ~/confs/flume01-interceptor.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
#############################################################################################
flume02-interceptor.conf
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#sources
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 6666
##sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
##channels
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
##bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
flume-ng agent -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -n a1 -f ~/confs/flume02-interceptor.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
#############################################################################################
flume03-interceptor.conf
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#sources
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 7777
##sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
##channels
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
##bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
flume-ng agent -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -n a1 -f ~/confs/flume03-interceptor.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
#############################################################################################
flume04-interceptor.conf
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#sources
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 8888
##sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
##channels
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
##bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
flume-ng agent -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -n a1 -f ~/confs/flume04-interceptor.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
#sources
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /home/suxichuan/flume/taildir_position.json
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /home/suxichuan/behavior/log
#channels
a1.channels.channel1.type = org.apache.flume.channel.kafka.KafkaChannel
a1.channels.channel1.kafka.bootstrap.servers = hadoop102:9092,hadoop103:9092,hadoop104:9092
a1.channels.channel1.kafka.topic = ods_behavor_log
a1.channels.channel1.kafka.consumer.group.id = ods_behavor_group_1
以上就是,Flume基础学习内容,后续会根据学习的规划调整笔记更新的内容。