Oracle学习基础
PL/SQL developer安装
1、安装PL/SQL developer程序,安装目录不要出现中文。
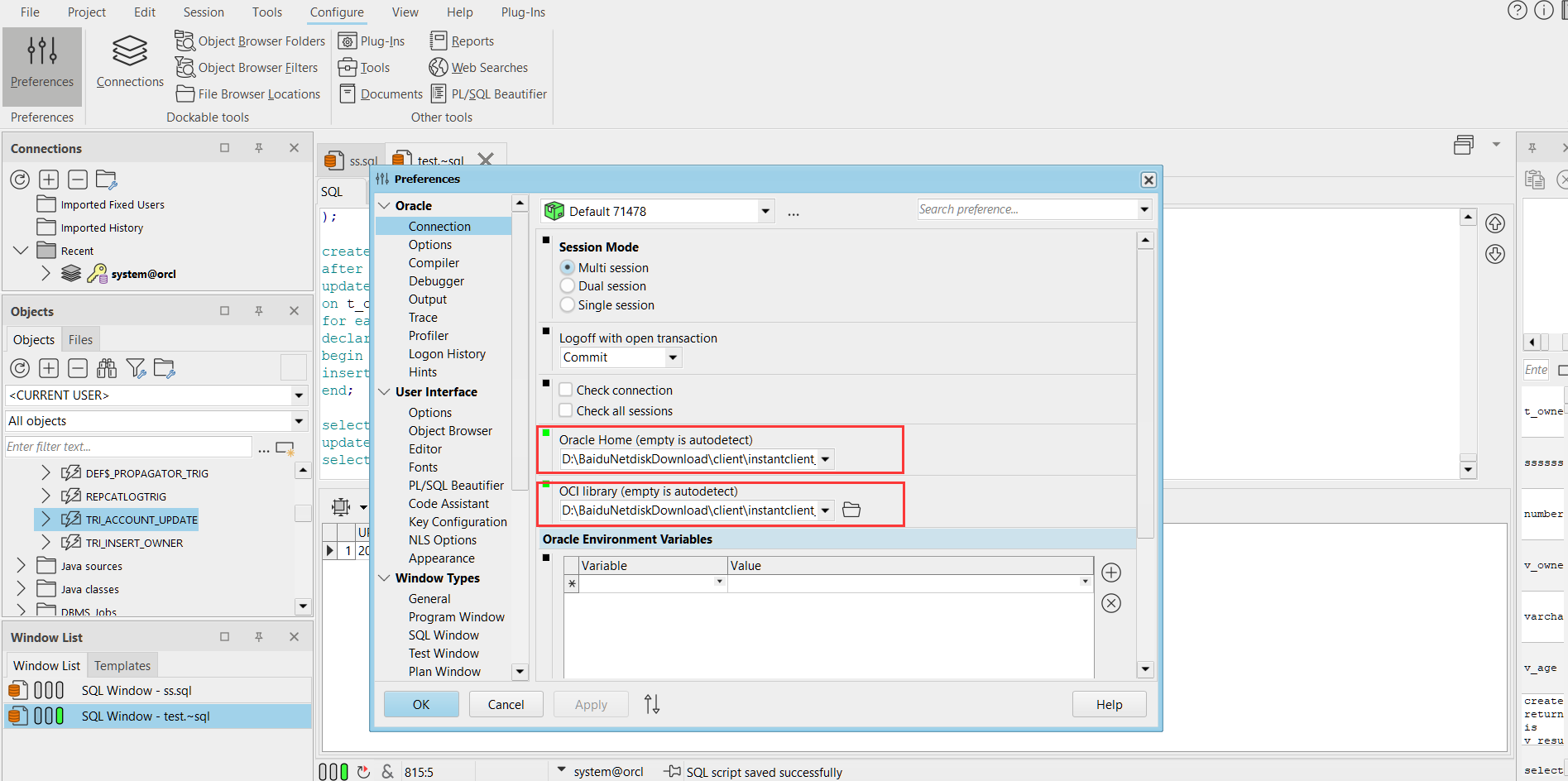
2、配置客户端路径:点击PL/SQL developer界面的Configure->Preferences->oracle配置的connect属性配置。,和
指定Oracle Home 路径:D:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\client\instantclient_12_1
指定OCI library路径:D:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\client\instantclient_12_1\oci.dll
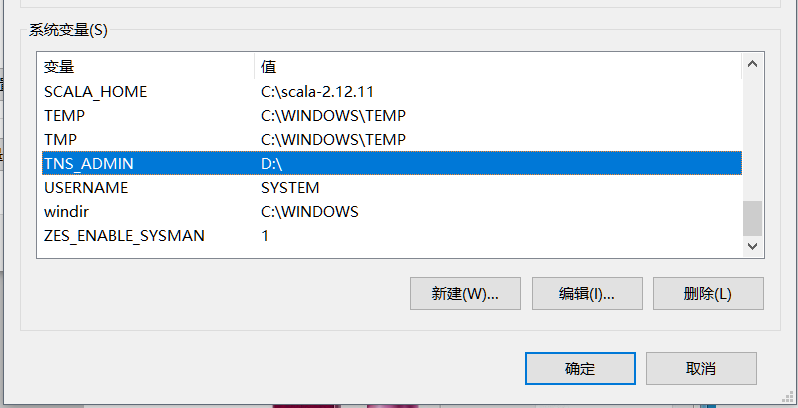
3、在 ORACLE 的以下安装目录中找到 tnsnames.ora 文件,拷贝到本地电脑的 D盘根目录。打开 tnsnames.ora 文件编辑配置oracle所在的服务器IP地址,设置环境变量 TNS_ADMIN 为 D 盘根目录( tnsnames.ora 所在目录 )
4、中文编码设置查看服务器端编码
1 | SQL:select userenv('language') from dual; |
我实际查到的结果为:AMERICAN_AMERICA.ZHS16GBK
5、配置环境变量,计算机->属性->高级系统设置->环境变量->新建,设置变量名:NLS_LANG,变量值:第 1 步查到的值,
AMERICAN_AMERICA.ZHS16GBK
1、数据类型
number 数值类型
1 | number(5) 最大值99999 |
字符串类型
1 | char 固定长度的字符类型,最多存储2000个字节 |
日期类型
1 | sysdate 日期时间型,精确到秒 |
二进制类型
1 | clob 存储字符,最大可以存4个G |
2、DDL操作
用SQLPLUS连接Oracle的连接字符串
1 | sqlplus system/local123@192.168.157.129:1521/orcl |
创建表空间
1 | create tablespace xxxx |
创建用户
1 | create user 用户名 |
用户赋予权限
1 | grant dba to 用户名 给xxx用户授予DBA权限 |
表的创建
1 | create table 表名( |
表的修改
1 | desc tablename 查看表的详情 |
清空表
1 | truncate table tablename; 删除表再重构表 |
删除表
1 | drop table tablename; |
3、DML操作
insert操作
1 |
|
update数据修改
1 | update 表名 set 字段=新值,字段=新值 where 条件; |
delete删除数据
1 | #delete from tablename where 条件 |
注意增删改查操作完成后记得commit提交事务
导入导出
数据的导出
1 | expdp(impdp) 用户名/密码@连接地址:端口/服务名 [schemas|owner]=用户名 [dumpfile|file]=file1.dmp logfile=file1.log directory=testdata1 remap_schema=test:test; |
1 | 通过@F:\website\oraok\ot\11g\ot_drop.sql 导入F盘下的\website\oraok\ot\11g\目录下的ot_drop.sql文件 |
4、DML练习
1 | select tac.areaid,sum(tac.money),ta.name from t_account tac,t_area ta where tac.areaid=ta.id group by tac.areaid,ta.name; |
简单查询
1 | select * from t_owners; |
连接查询
1 | #多表内连接 |
子查询
where子句中的子查询
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16#单行子查询
#查询 2023 年 6 月用水量大于平均值的台账记录
select avg(usenum) from t_account where month=6;
select usenum from t_account where usenum>(select avg(usenum) from t_account where month=6) and month=6;
#多行子查询
select * from t_address where id in (1001,1002);
#查询地址含有“草”的业主的信息
select id from t_address where name like '%草%';
select * from t_owners where addressid in (select id from t_address where name like '%江安河%');
#查询地址不含有“草”的业主的信息
select id from t_address where name not like '%草%';
select * from t_owners where addressid in (select id from t_address where name not like '%草%');
select * from t_onwers where addressid not in(select id from t_address where name like '%草%');
#from子句中的子查询
from子查询为多行子查询
1
2
3#查询显示业主编号,业主名称,业主类型名称,条件为业主类型为”居民”,使用子查询实现。
select id,name,ownertypename from (select twn.*,tt.name ownertypename from t_owners twn,t_ownertype tt where twn.ownertypeid=tt.id and tt.name='居民')select 子句中的子查询
1
2
3
4
5
6
7#列出业主信息,包括 ID,名称,所属地址。
select id,name,(select name from t_address where id=addressid) addressname from t_owners;
#列出业主信息,包括 ID,名称,所属地址,所属区域
select id,name,
(select name from t_address where id=addressid) addressname,
(select (select name from t_area where id=areaid) from t_address where id=addressid) areaname
from t_owners;分页查询
使用rownum伪列来完成分页查询的功能。
1
2
3
4
5#分页查询台账表 T_ACCOUNT,每页 10 条记录
select rownum,t.* from t_account t where rownum<=5;
#查询5到10的数据
#子查询里rownum小于较大值,外面rownum大于较小值
select rownum,t.* from (select rownum r,t.* from t_account t where rownum<=20) t where r<=5;
5、函数
字符函数
1 | select ascii('a') from dual;ASCII() 返回字符的十进制数; |
日期函数
1 | sysdate 返回系统当前时间 |
数值函数
1 | select abs(value) from dual;绝对值 |
6、表空间巡检
查询视图dba_data_files
1 | file_name:表空间数据文件的位置 |
查询视图dba_free_space
1 | tablespace_name:表空间名称 |
7、视图
概念:视图是一种数据库对象,是从一个或者多个数据表或视图中导出的虚表,视图所对应的数据并不真正地存储在视图中,而是存储在所引用的数据表中,视图的结构和数据是对数据表进行查询的结果。
优点:
- 简化数据操作:视图可以简化用户处理数据的方式。
- 着重于特定数据:不必要的数据或敏感数据可以不出现在视图中。
- 视图提供了一个简单而有效的安全机制,可以定制不同用户对数据的访问权限。
- 提供向后兼容性:视图使用户能够在表的架构更改时为表创建向后兼容接口。
创建和修改视图
1 | create [or replace] [force] view view_name |
视图其实是一个虚拟的表,它的数据其实来自于表。如果更改了视图的数据,表的数据也自然会变化,更改了
表的数据,视图也自然会变化。
删除视图
1 | drop view view_name; |
带检查约束的视图
1 | create or replace view t_account_v2 |
只读视图的创建与使用
指定 WITH READ ONLY 选项,这样创建的视图就是一个只读视图
1 | create or replace view t_account_v2 |
创建不存在基表的视图
有的时候,创建视图时的表可能并不存在,但是以后可能会存在,此时需要创建这样的视图,需要添加 FORCE 选项
1 | create or replace force view t_temp_vi |
查询所有的视图
1 | select * from user_views; |
复杂视图的创建与使用
复杂视图,就是视图的 SQL 语句中,有聚合函数或多表关联查询。
1 | #1、多表关联查询的视图 |
物化视图
视图是一个虚拟表(也可以认为是一条语句),基于它创建时指定的查询语句返回的结果集。每次访问它都会导致这个查询语句被执行一次。为了避免每次访问都执行这个查询,可以将这个查询结果集存储到一个物化视图(也叫实体化视图)。物化视图与普通的视图相比的区别是物化视图是建立的副本,它类似于一张表,需要占用存储空间。而对一个物化视图查询的执行效率与查询一个表是一样的。
- 创建物化视图语法
1 | create meterialized view view_name |
- 创建手动刷新的物化视图
1 | create meterialized view mv_v1 |
- 创建自动刷新的物化视图
1 | create materialized view mv_v3 |
- 创建时不生成数据的物化视图
1 | create materailized view mv_v4 |
- 删除物化视图
1 | drop materialized view view_name; |
- 创建增量刷新的物化视图
如果创建增量刷新的物化视图,必须首先创建物化视图日志
1 | #创建物化视图日志 |
8、序列
序列是 ORACLE 提供的用于产生一系列唯一数字的数据库对象。
创建序列语法
1 | create sequence sequence_name; |
通过序列的伪列来访问序列的值,NEXTVAL 返回序列的下一个值,CURRVAL 返回序列的当前值
注意:我们在刚建立序列后,无法提取当前值,只有先提取下一个值时才能再次提取当前值。
1 | create sequence sequence_one; |
创建复杂序列
- 语法:
1 | create sequence sequence_one |
- 创建有最大值的非循环序列
1 | create sequence seq_1 |
- 有最大值的循环序列
1 | create sequence seq_2 |
注意:CACHE <= CEIL((MAXVALUE - MINVALUE) / ABS(INCREMENT))
例如:cache <=ceil(100-20)/abs(20)
修改和删除序列
修改序列:使用 ALTER SEQUENCE 语句修改序列,不能更改序列的 STARTWITH 参数
1 | ALTER SEQUENCE 序列名称 MAXVALUE 5000 CYCLE; |
删除序列
1 | DROP SEQUENCE 序列名称; |
9、同义词
同义词实质上是指定方案对象的一个别名。通过屏蔽对象的名称和所有者以及对分布式数据库的远程对象提供位置透明性,同义词可以提供一定程度的安全性。同时,同义词的易用性较好,降低了数据库用户的 SQL 语句复杂度。
同义词允许基对象重命名或者移动,这时,只需对同义词进行重定义,基于同义词的应用程序可以继续运行而无需修改。
同义词本身不涉及安全,当你赋予一个同义词对象权限时,你实质上是在给同义词的基对象赋予权限,同义词只是基对象的一个别名。
创建与使用同义词
1 | create [public] SYNONYM synonym for object |
10、索引
索引是用于加速数据存取的数据对象。合理的使用索引可以大大降低 i/o 次数,从而提高数据访问性能。
索引是需要占据存储空间的,也可以理解为是一种特殊的数据。形式类似于下图的一棵“树”,而树的节点存储的就是每条记录的物理地址,也就是我们提到的伪列(ROWID)
普通索引
1 | create index index_name on table_name(column_name);#根据某张表的某列来创建索引。 |
唯一索引
如果我们需要在某个表某个列创建索引,而这列的值是不会重复的。这是我们可以创建唯一索引。
语法
1 | create unique index index_name on table_name(column_name); |
复合索引
1 | create index index_name on table_name(column_name,column_name); |
反向键索引
应用场景:当某个字段的值为连续增长的值,如果构建标准索引,会形成歪脖子树。这样会增加查询的层数,性能会下降。建立反向键索引,可以使索引的值变得不规则,从而使索引树能够均匀分布。
1 | create index 索引名称 on 表名(列名) reverse; |
位图索引
- 使用场景:位图索引适合创建在低基数列上
- 位图索引不直接存储 ROWID,而是存储字节位到 ROWID 的映射
- 优点:减少响应时间,节省空间占用
1 | create bitmap index index_name table_name(column_name); |
11、PL/SQL
PL/SQL(Procedure Language/SQL)是 Oracle 对 sql 语言的过程化扩展,指在 SQL 命令语言中增加了过程处理语句(如分支、循环等),使 SQL 语言具有过程处理能力。把 SQL 语言的数据操纵能力与过程语言的数据处理能力结合起来,使得 PLSQL 面向过程但比过程语言简单、高效、灵活和实用。
基本语法结构
1 | [declare --声明变量] |
变量
1 | 声明变量的语法 |
select into方式赋值
1 | select 列名 into 变量名 from 表名 where 条件; |
注意:结果必须是一条记录 ,有多条记录和没有记录都会报错
1 | select usenum,num0,num1 from t_account where year=2023 and id=1; |
属性类型
%TYPE 引用型 作用:引用某表某列的字段类型
1 | declare |
%ROWTYPE 记录型 ,上例中的例子可以用下面的代码代替作用: 标识某个表的行记录类型
1 | declare |
异常
在运行程序时出现的错误叫做异常,发生异常后,语句将停止执行,控制权转移到 PL/SQL 块的异常处理部分
异常有两种类型:
- 预定义异常 - 当 PL/SQL 程序违反 Oracle 规则或超越系统限制时隐式引发。
- 用户定义异常 - 用户可以在 PL/SQL 块的声明部分定义异常,自定义的异常通过 RAISE 语句显式引发。
oracle预定义的异常21个
| 系统异常 | 产生原因 |
|---|---|
| ACCESS_INTO_NULL | 未定义对象 |
| CASE_NOT_FOUND | CASE 中若未包含相应的 WHEN ,并且没有设置 ELSE 时 |
| COLLECTION_IS_NULL | 集合元素未初始化 |
| CURSER_ALREADY_OPEN | 游标已经打开 |
| DUP_VAL_ON_INDEX | 唯一索引对应的列上有重复值 |
| INVALID_CURSOR | 在不合法的游标上进行操作 |
| INVALID_NUMBER | 内置的SQL语句不能将字符转化为数字 |
| NO_DATA_FOUND | 使用select into 没有行返回行 |
| TOO_MANY_ROWS | 使用select into 有多行数据返回 |
| ZERO_DIVIDE | 除数为0 |
| SUBSCRIPT_BEYOND_COUNT | 元素下标超过嵌套表或 VARRAY 的最大值 |
| SUBSCRIPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT | 使用嵌套表或 VARRAY 时,将下标指定为负数 |
| VALUE_ERROR | 赋值时,变量长度不足以容纳实际数据 |
| LOGIN_DENIED | PL/SQL 应用程序连接到 oracle 数据库时,提供了不正确的用户名或密码 |
| NOT_LOGGED_ON | PL/SQL 应用程序在没有连接 oralce 数据库的情况下访问数据 |
| PROGRAM_ERROR | PL/SQL 内部问题,可能需要重装数据字典& PL/SQL 系统包 |
| ROWTYPE_MISMATCH | 宿主游标变量与 PL/SQL 游标变量的返回类型不兼容 |
| SELF_IS_NULL | 使用对象类型时,在 NULL对象上调用对象方法 |
| STORAGE_ERROR | 运行 PL/SQL 时,超出内存空间 |
| SYS_INVALID_ID | 无效的 ROWID 字符串 |
| TIMEOUT_ON_RESOURCE | Oracle 在等待资源时超时 |
语法结构:
1 | exception |
1 | declare |
条件判断
1 | #基本语法1 |
需求:设置三个等级的水费 5 吨以下 2.45 元/吨 5 吨到 10 吨部分 3.45 元/吨 ,超过 10 吨部分 4.45 ,根据使用水费的量来计算阶梯水费。
1 | declare |
循环
- 无条件循环
1 | loop |
2.条件循环
1 | while 条件 |
3.for循环
1 | #基本语法 |
游标
游标是系统为用户开设的一个数据缓冲区,存放 SQL 语句的执行结果。我们可以把游标理解为 PL/SQL 中的结果集。
在声明区声明游标,语法如下:
1 | cursor 游标名称 is SQL 语句; |
使用游标语法
1 | open 游标名称 |
需求:打印业主类型为 1 的价格表
1 | declare |
带参数的游标
1 | declare |
for 循环提取游标值
1 | declare |
12、存储函数
存储函数又称为自定义函数。可以接收一个或多个参数,返回一个结果。在函数中我们可以使用 PL/SQL 进行逻辑的处理。
存储函数语法结构
1 | create or replace function 函数名称(参数名称 参数类型, 参数名称 参数类型, ...) |
示例
1 | create function pingping(v_name varchar2,v_age number) |
需求:查询业主 ID,业主名称,业主地址,业主地址使用刚才我们创建的函数来实现。
1 | create function ss(v_id number) return varchar2 |
13、存储过程
概念
存储过程是被命名的 PL/SQL 块,存储于数据库中,是数据库对象的一种。应用程序可以调用存储过程,执行相应的逻辑。
存储过程与存储函数都可以封装一定的业务逻辑并返回结果,存在区别如下:
1、存储函数中有返回值,且必须返回;而存储过程没有返回值,可以通过传出参数返回多个值。
2、存储函数可以在 select 语句中直接使用,而存储过程不能。过程多数是被应用程序所调用。
3、存储函数一般都是封装一个查询结果,而存储过程一般都封装一段事务代码。
语法
1 | create or replace procedure 存储过程名字(参数1 类型,参数2 类型) |
参数只指定类型,不指定长度
过程参数的三种模式:IN 传入参数(默认),OUT 传出参数 ,主要用于返回程序运行结果,IN OUT 传入传出参数
案例
1、创建不带传出参数的存储过程:添加业主信息
1 | create sequence owner_sequence start with 1010; |
2、创建带传出参数的存储过程
1 | create or replace procedure owners_add_with_out(v_name varchar2,v_addressid number,v_housenumber varchar2,v_watermeter varchar2,v_type varchar2,v_id out number) |
14、触发器
概念
数据库触发器是一个与表相关联的、存储的 PL/SQL 程序。每当一个特定的数据操作语句(Insert,update,delete)在指定的表上发出时,Oracle 自动地执行触发器中定义的语句序列。
触发器可用于
- 数据确认
- 实施复杂的安全性检查
- 做审计,跟踪表上所做的数据操作等
- 数据的备份和同步
触发器分类
- 前置触发器(BEFORE)
- 后置触发器(AFTER)
触发器语法
1 | create or replace trigger 触发器名字 |
作用是标注此触发器是行级触发器还是语句级触发器
在触发器中触发语句与伪记录变量的值
| 触发语句 | :old | :new |
|---|---|---|
| insert | 所有字段都是空的(null) | 将要插入的数据 |
| update | 更新以前该行的值 | 更新后的值 |
| delete | 删除以前该行的值 | 所有字段都是空的(null) |
案例
1、前置触发器
需求:当用户输入本月累计表数后,自动计算出本月使用数 。
1 | create or replace trigger tri_account_update |
2、后置触发器
需求:当用户修改了业主信息表的数据时记录修改前与修改后的值
1 |
|